Results
Years since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom

Inclusion criterion was onset of first non-Raynaud symptom <7 years before screening. Actual maximum was 7.2 years.
Baseline characteristics in subgroups by time since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom
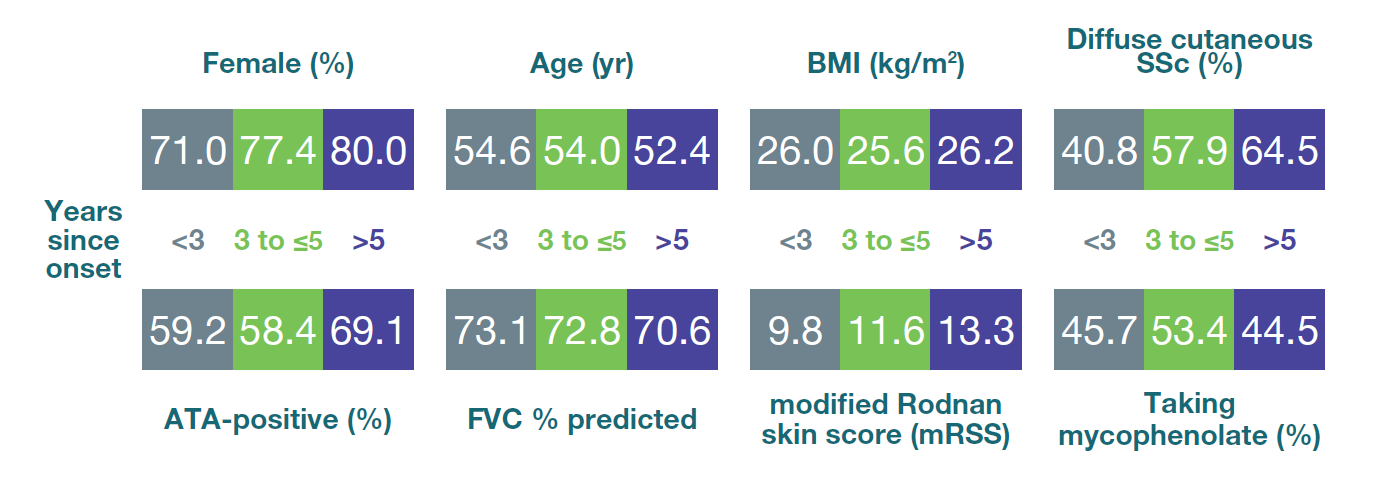
Mean or % of patients
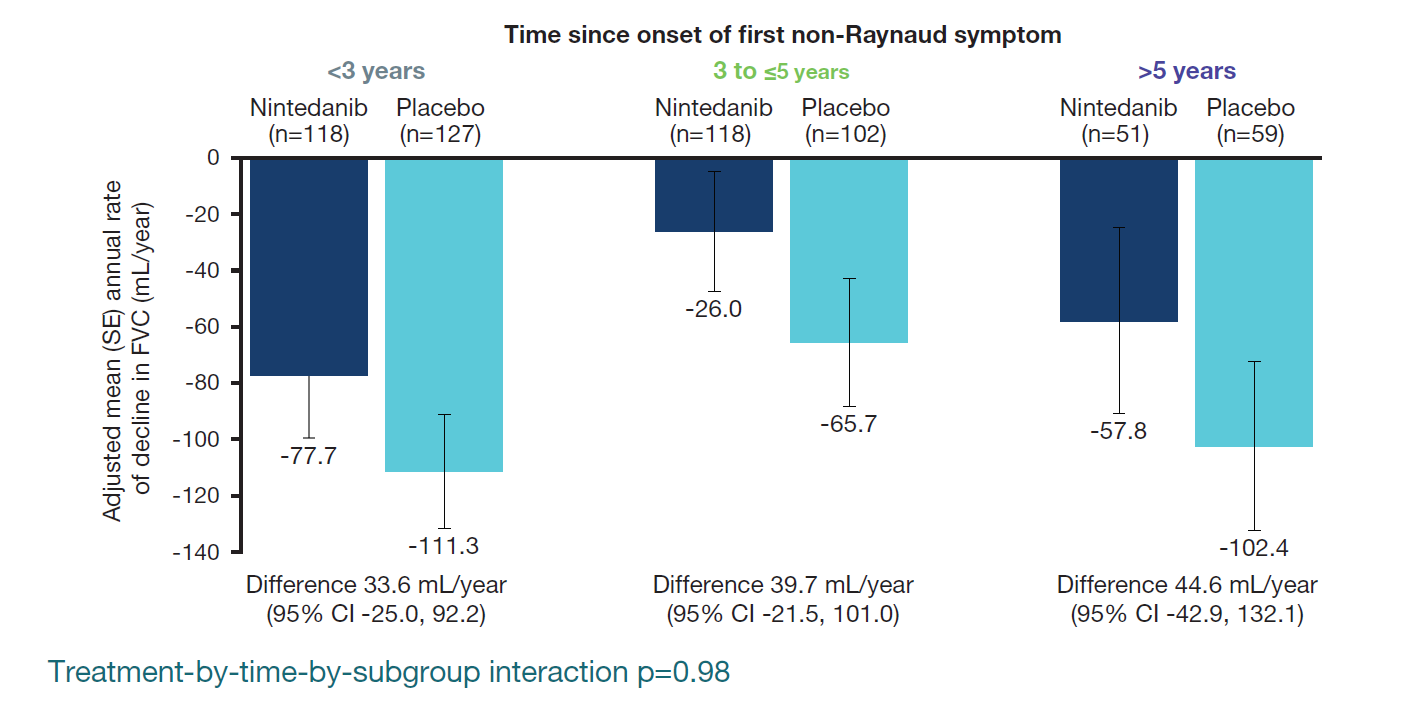
Annual rate of decline in FVC (mL/year)
- The effect of nintedanib vs placebo on reducing the annual rate of decline in FVC was consistent across the subgroups by time since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Rate of decline in FVC (mL/year) over 52 weeks in subgroups by time since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom
Categorical declines in FVC over 52 weeks
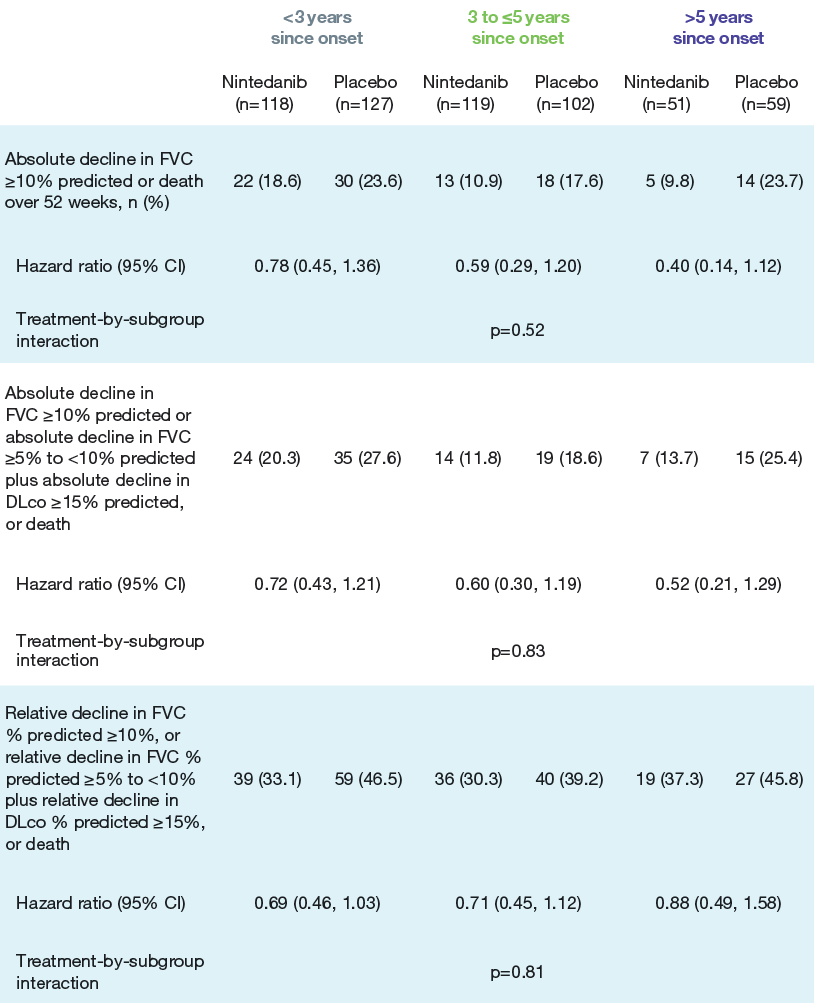
- No heterogeneity was detected in the effect of nintedanib versus placebo on categorical declines in FVC or time to composite outcomes based on lung function decline and death across the subgroups (Figure 2; Table).
Figure 2. Absolute and relative declines in FVC in subgroups by time since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom
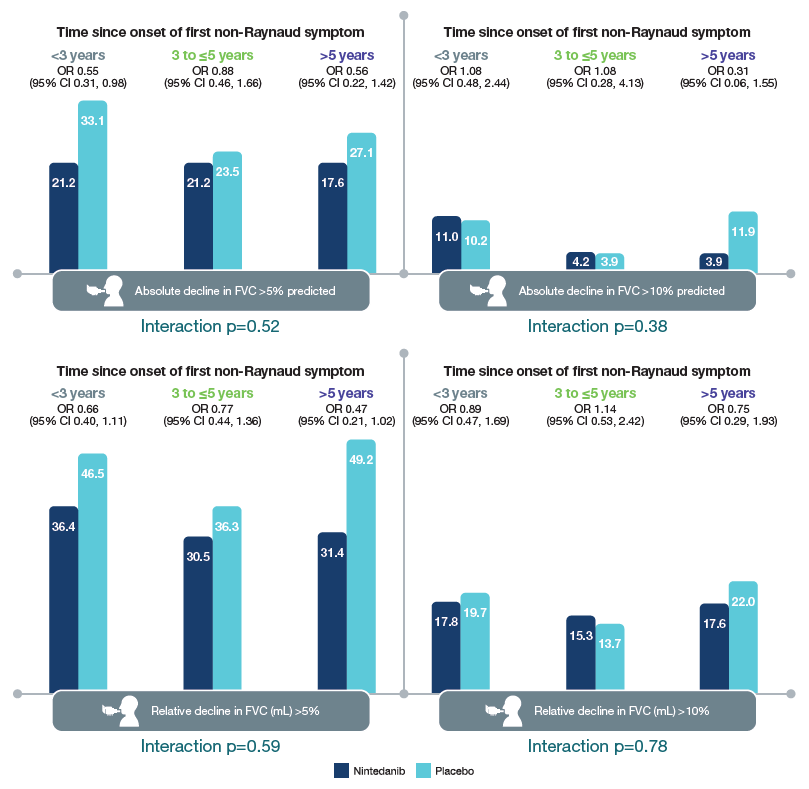
OR, odds ratio.
Table. Time to composite outcomes in subgroups by time since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom
Adverse events
- The adverse event profile of nintedanib was consistent across the subgroups (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Most frequent adverse events in subgroups by time since onset of first non-Raynaud symptom
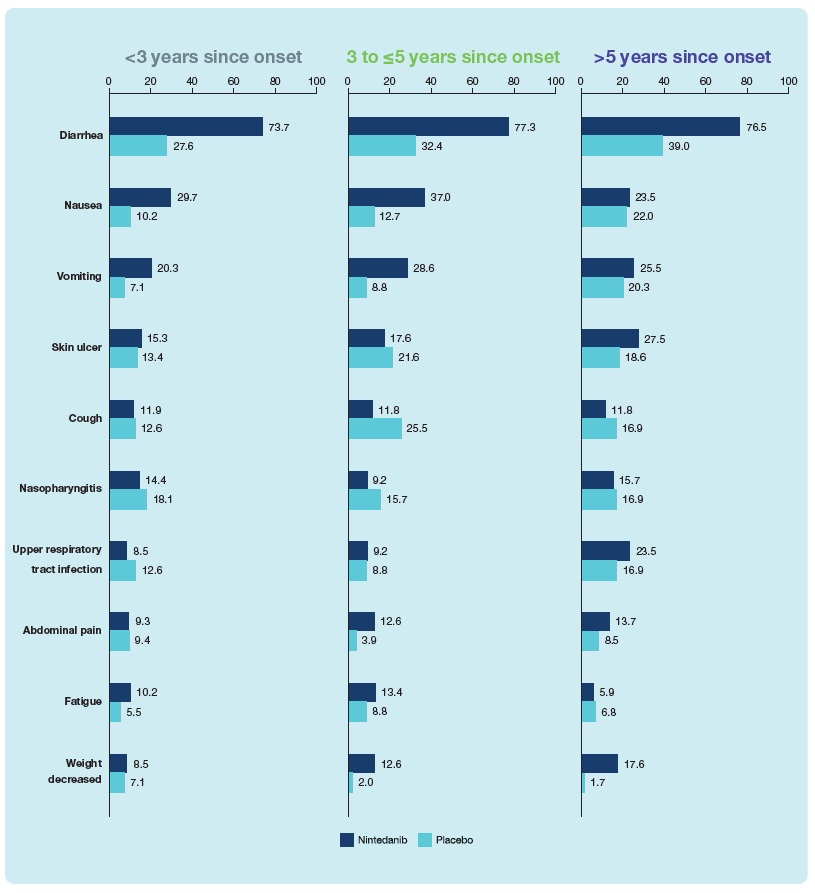
AEs reported (irrespective of causality) in >10% of subjects in either treatment group in the overall population, coded using preferred terms in the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA). Data are % of subjects with ≥1 such AE, reported over 52 weeks (or until 28 days after last trial drug intake in patients who discontinued trial drug before week 52).