Results
Patients
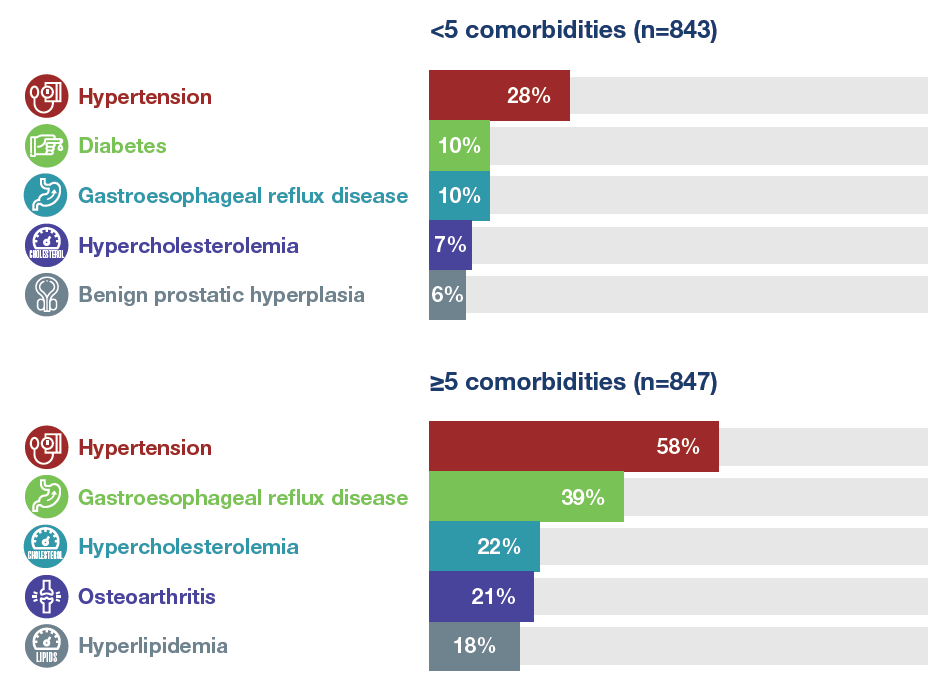
Most frequent comorbidities in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
Baseline characteristics of patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
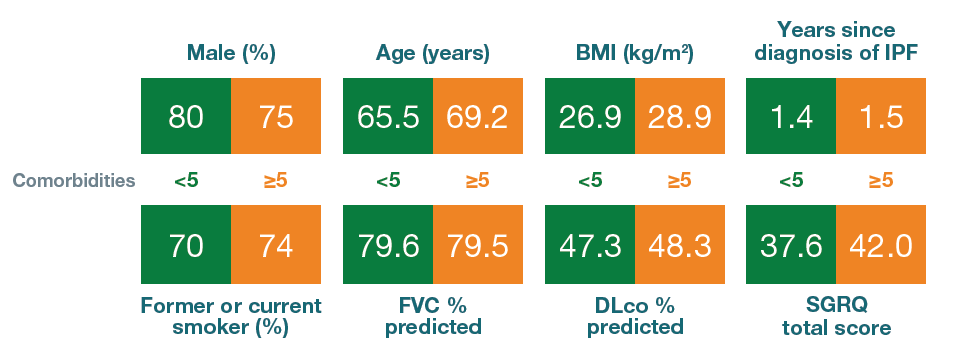
Mean or % of patients
Exposure
- Mean (SD) exposure to nintedanib and placebo was 8.8 (4.1) and 8.2 (4.3) months in patients with ≥5 comorbidities and 9.2 (4.1) and 8.1 (4.4) months in patients with <5 comorbidities at baseline, respectively.
Annual rate of decline in FVC
- Nintedanib reduced the annual rate of decline in FVC (mL/year) in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline, with no significant difference in its treatment effect between the subgroups.
Annual rate of decline in FVC (mL/year) in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
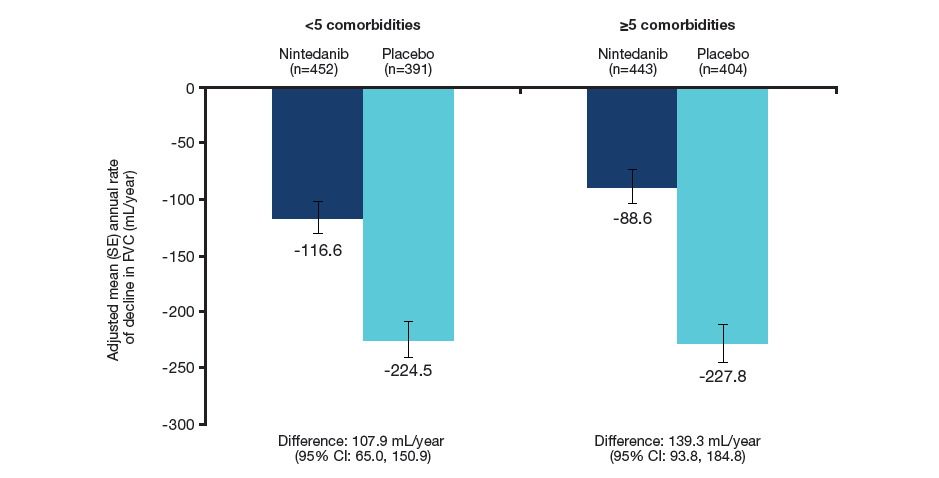
Treatment-by-time-by-subgroup interaction p=0.41.
Change in SGRQ total score
- Over 52 weeks, SGRQ total score increased (worsened) to a greater extent in patients with ≥5 than <5 comorbidities at baseline, particularly in the placebo group.
Change in SGRQ total score at week 52 in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
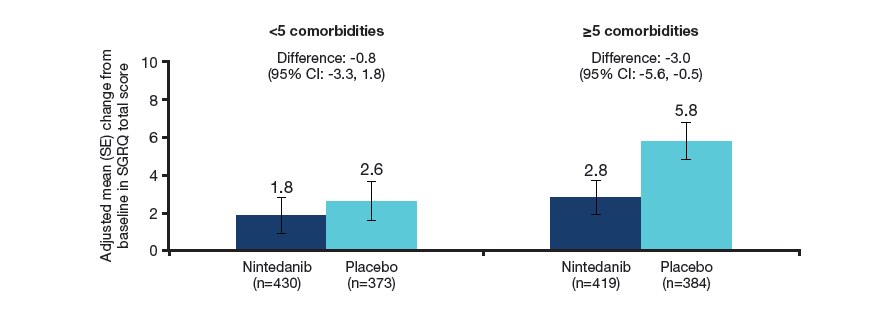
The SGRQ total score ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating worse health-related quality of life.
Treatment-by-subgroup interaction p=0.22.
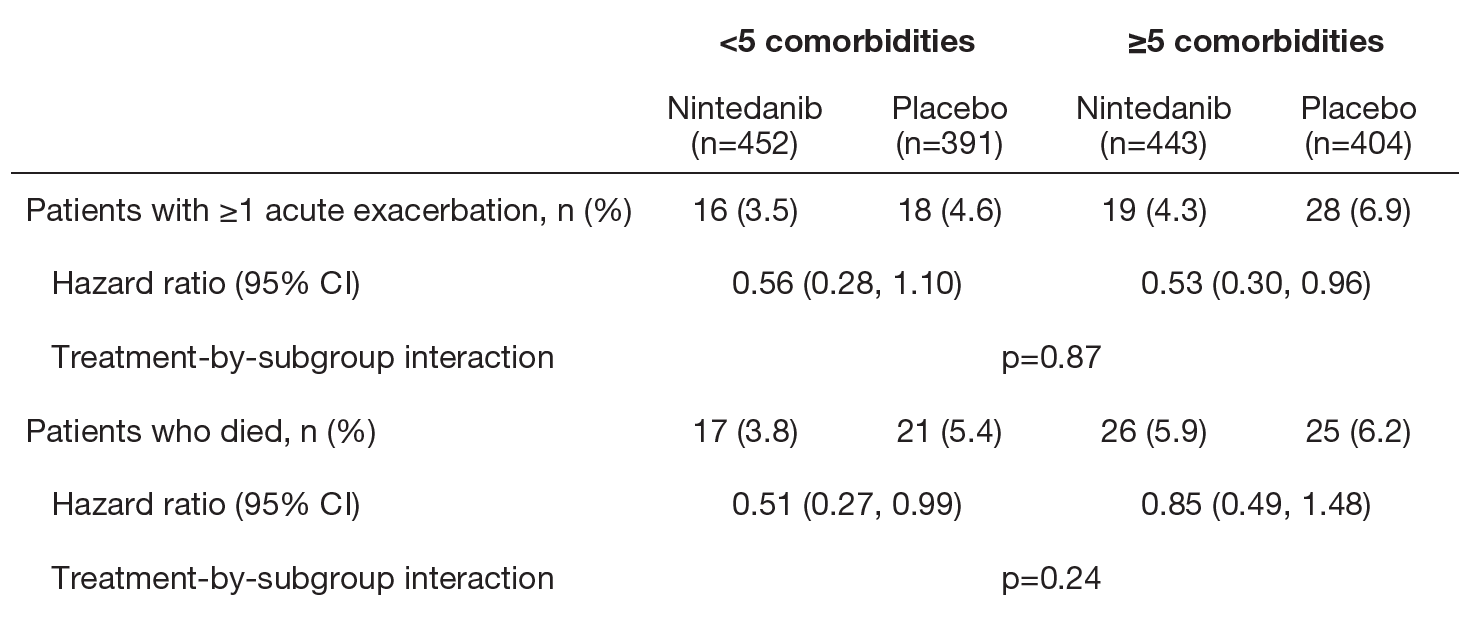
Acute exacerbations and deaths
- The effect of nintedanib versus placebo in reducing the risk of a first acute exacerbation and the risk of death was consistent between patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline.
Time to first acute exacerbation and death in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
Adverse events
- The adverse event profile of nintedanib was similar between subgroups by number of comorbidities at baseline. In both treatment groups, diarrhea and nausea were reported more frequently in patients with ≥5 than <5 comorbidities at baseline.
Most frequent adverse events in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
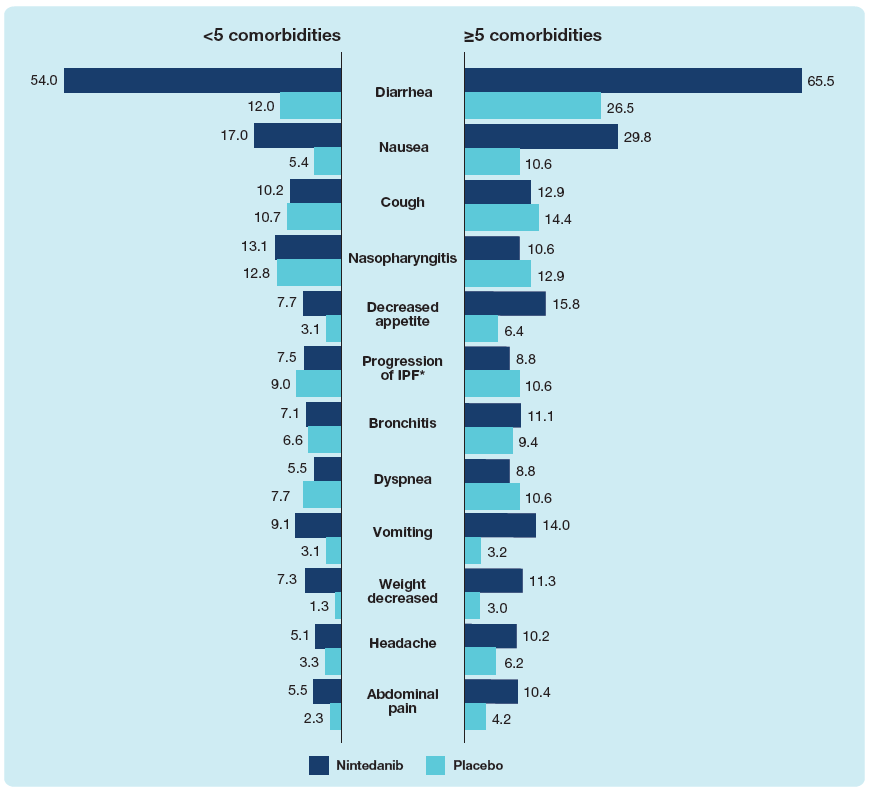
Data are % of patients with ≥1 such adverse event reported (irrespective of causality) in >10% of patients in either subgroup, coded using preferred terms in the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA). *Corresponded to MedDRA term ‘IPF’, which included disease worsening and acute exacerbations of IPF.
Proportions of patients with adverse events leading to discontinuation of trial drug and severe adverse events in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
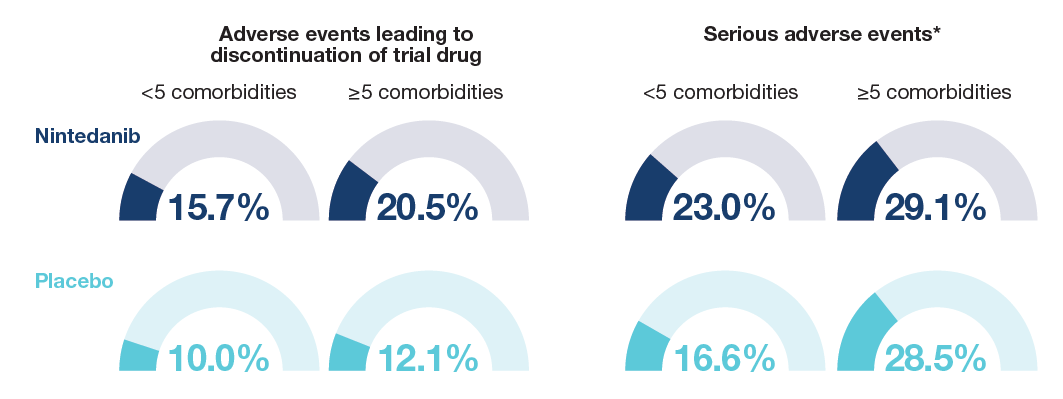
Data are % of subjects with ≥1 such adverse event. *Events that resulted in death, were life-threatening, resulted in hospitalization or prolonged hospitalization, resulted in persistent or clinically significant disability or incapacity, were a congenital anomaly or birth defect, or were deemed serious for any other reason.
Most frequent adverse events leading to discontinuation of trial drug in patients with <5 and ≥5 comorbidities at baseline
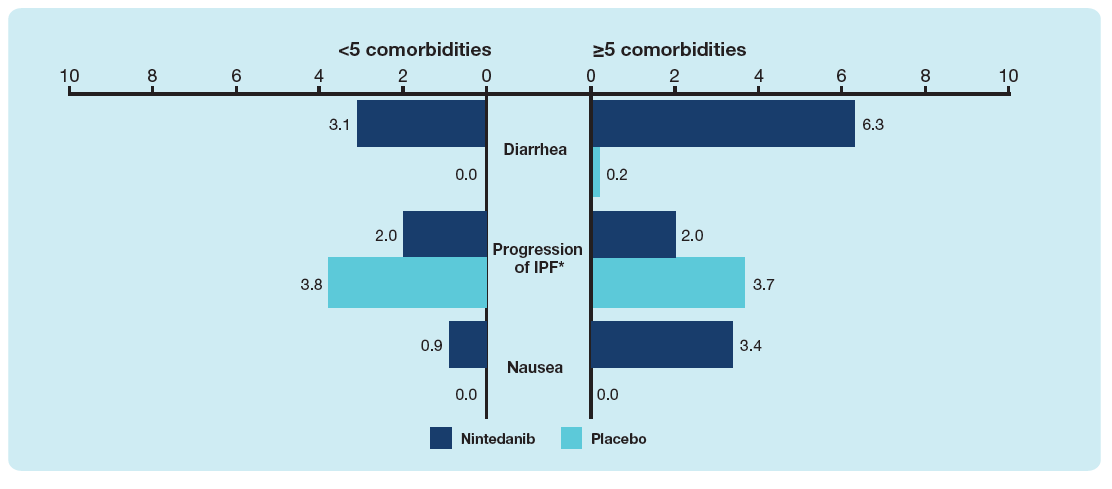
Data are % of patients with ≥1 adverse event leading to discontinuation of trial drug. Events reported in >2% of patients in either subgroup are shown. *Corresponded to MedDRA term ‘IPF’, which included disease worsening and acute exacerbations of IPF.